
Learn how to select ranges in a worksheet. The cell range also needs to include the return value you want to find. The first column in the cell range must contain the lookup_value. You can use a named range or a table, and you can use names in the argument instead of cell references. The range of cells in which the VLOOKUP will search for the lookup_value and the return value.
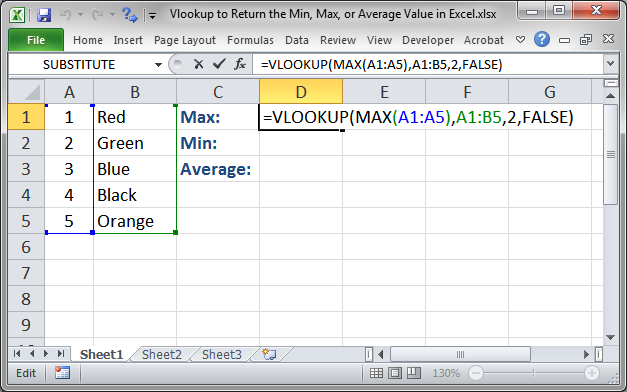
Lookup_value can be a value or a reference to a cell.
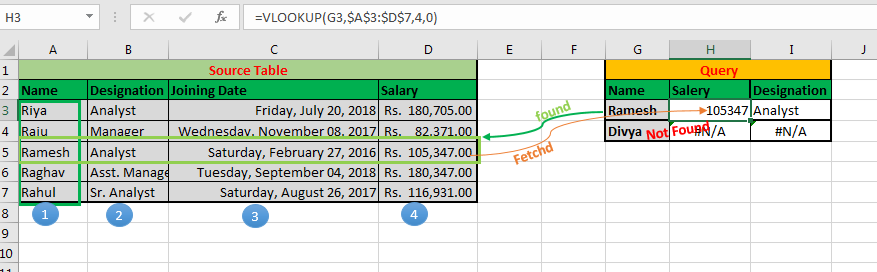
The value you want to look up must be in the first column of the range of cells you specify in the table_array argument.įor example, if table-array spans cells B2:D7, then your lookup_value must be in column B. =VLOOKUP(A2,’Client Details’!A:F,3,FALSE) VLOOKUP (lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, ) Use the LOOKUPVALUE function to return values by filter criteria.Use the VLOOKUP function to look up a value in a table. Use the RELATEDTABLE function to lookup a table with all rows related to the current row. Use the RELATED function to lookup values in a related table. The one that you choose depends on what you need your formula to do. These require a custom formula created using DAX, which includes several functions that perform similar lookups. There are a number of cases in Power Pivot in which you might want to lookup values in another table as part of a calculation-such as a calculated column or measure. This simple solution does have some requirements: The lookup column Region must be in a related table, and the Geography table cannot be hidden from the PivotTable Field List. You can simply add Region as a field to the PivotTable. Looking up values in another table is really quite easy, and in many cases you don’t need to create any formula at all.įor example, let's say you have a PivotTable in an Excel worksheet for analyzing sales data in your data model-and you want to slice based on regional data from a Region column in a Geography table. In Power Pivot, remember that you're working with a relational data model. DAX functions only take a column or a table as a reference. This is primarily because in Power Pivot, Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) functions don’t take a cell or cell range as a reference-as VLOOKUP does in Excel. But, you can’t use VLOOKUP in Power Pivot. One of the most popular functions in Excel formulas is VLOOKUP.

Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel 2021 Excel 2019 Excel 2016 Excel 2013 More.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
